Muscle Synergy-based Grasp Classification for Robotic Hand Prosthetics
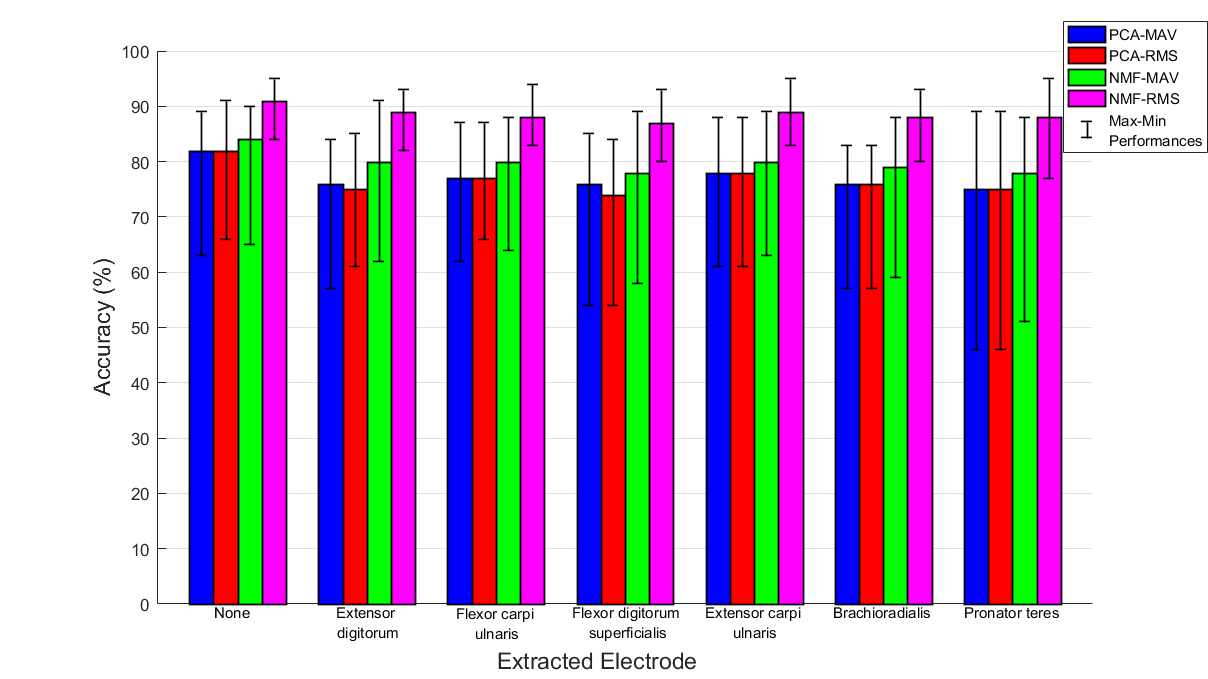
We present a comparison study for dimensionality reduction technique selection and EMG amplitude assumtion decision.
Click here for more information
Transfer Learning using Low-Dimensional Subspaces for EMG-based Classification of Hand Posture
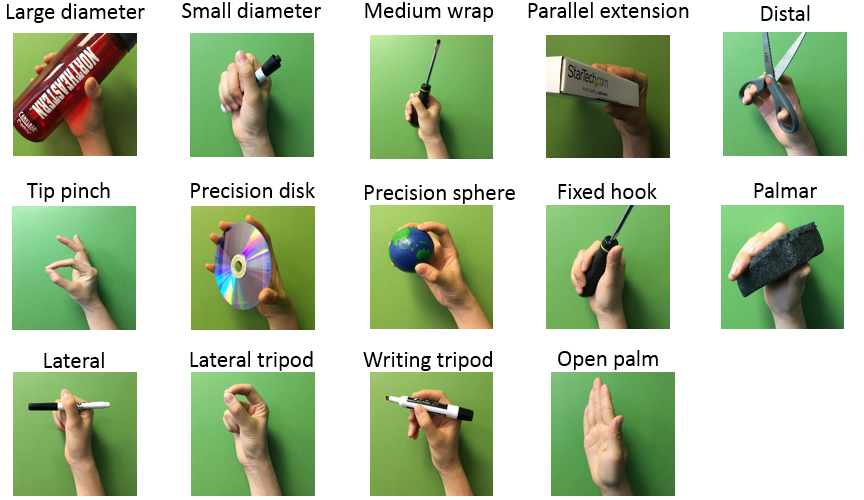

We investigate the ability to transfer synergy patterns across three different task domains, as described below.
We compare SVM vs. ELM classifiersfor this purpose and report on the sensitivity of ELM to the particular set of random initialization weights.
Click here for more information
Examining Invariance of Low-Dimensional Muscle Representation Across Tasks using a Classification Approach
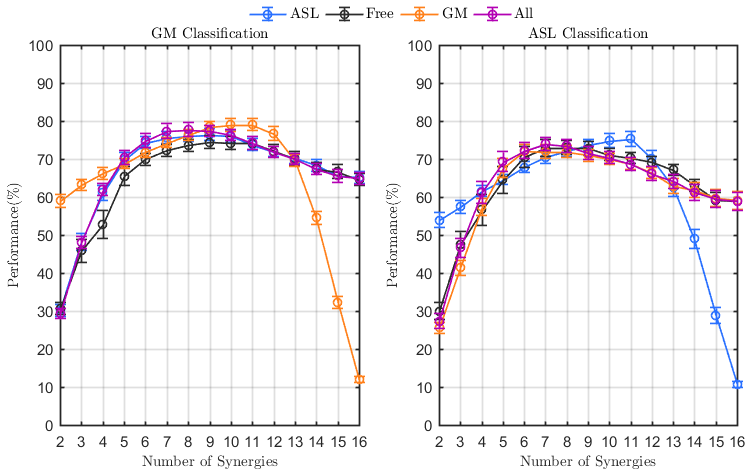
Three main questions are examined in this study: are muscle synergies generalizable for different tasks?,
are muscle synergies generalizable for different days?,
and are muscle synergiesgeneralizable for different subjects?
Click here for more information
DeepEMGNet: Intact to Amputee Transfer Learning Model for EMG-Based Hand Posture Classification
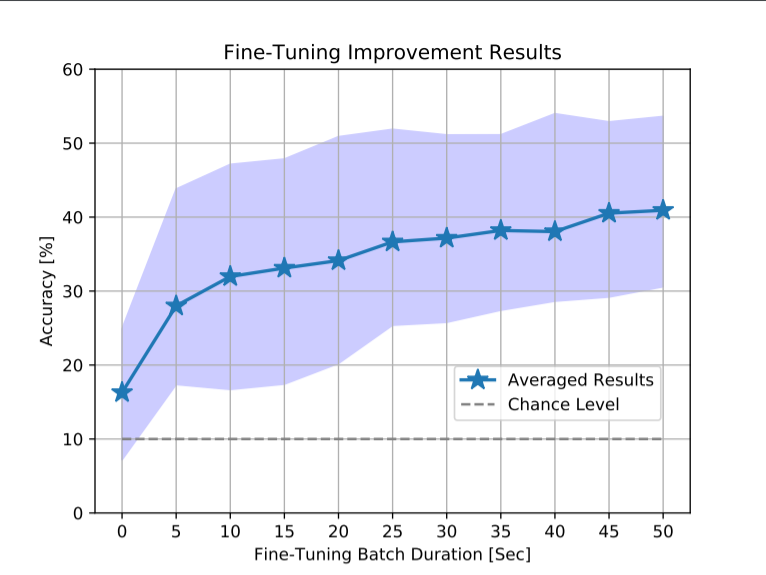
We propose a novel convolutional neural network encoder architecture, DeepEMGNet, that is built to extract subject-invariant, transferable representations from EMG signals.
Click here for more information
Real-time Myoelectrical Control of Prosthetic Hand
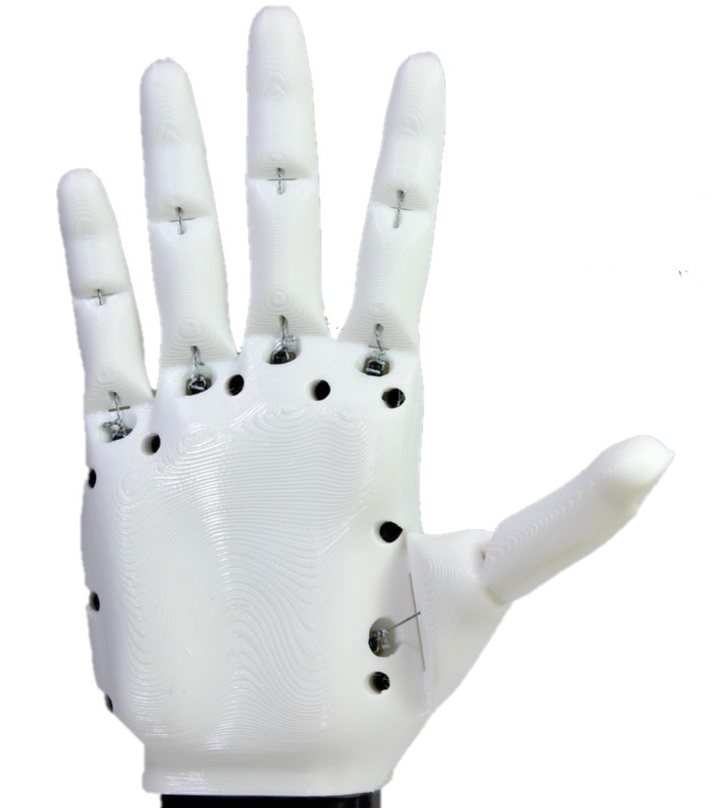
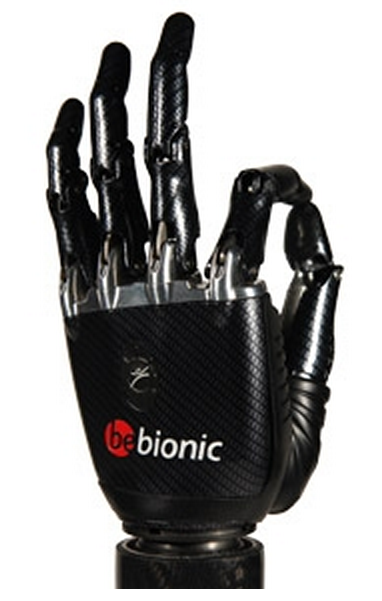

We present three stages of the real-time classification experiments are explained and supplementary visuals are provided.
Click here for more information
Force-Sensitive Prosthetic Hand with 3-axis Magnetic Force Sensors
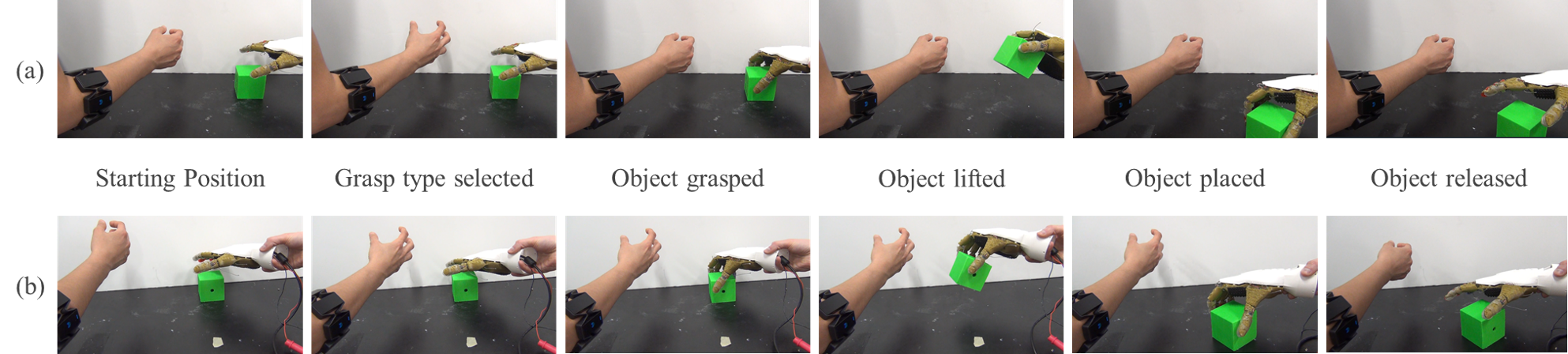
We present a 3D magnetic force sensor embedded in an open-source, affordable advanced prosthetic. Our 3D printable hand,
built off Open Bionics' open-source Ada hand, is underactuated to allow for compliant grasping. It additionally is equipped with embedded
custom 3-axis force sensors, enabling force control with the hand using shear and normal forces. To capture user intent, we use the Myo Armband
to acquire EMG data and employ an Extremely Randomized Tree Classifier to predict the user's grasp type.
Click here for more information
Kinematic Optimization of an Underactuated Anthropomorphic Prosthetic Hand
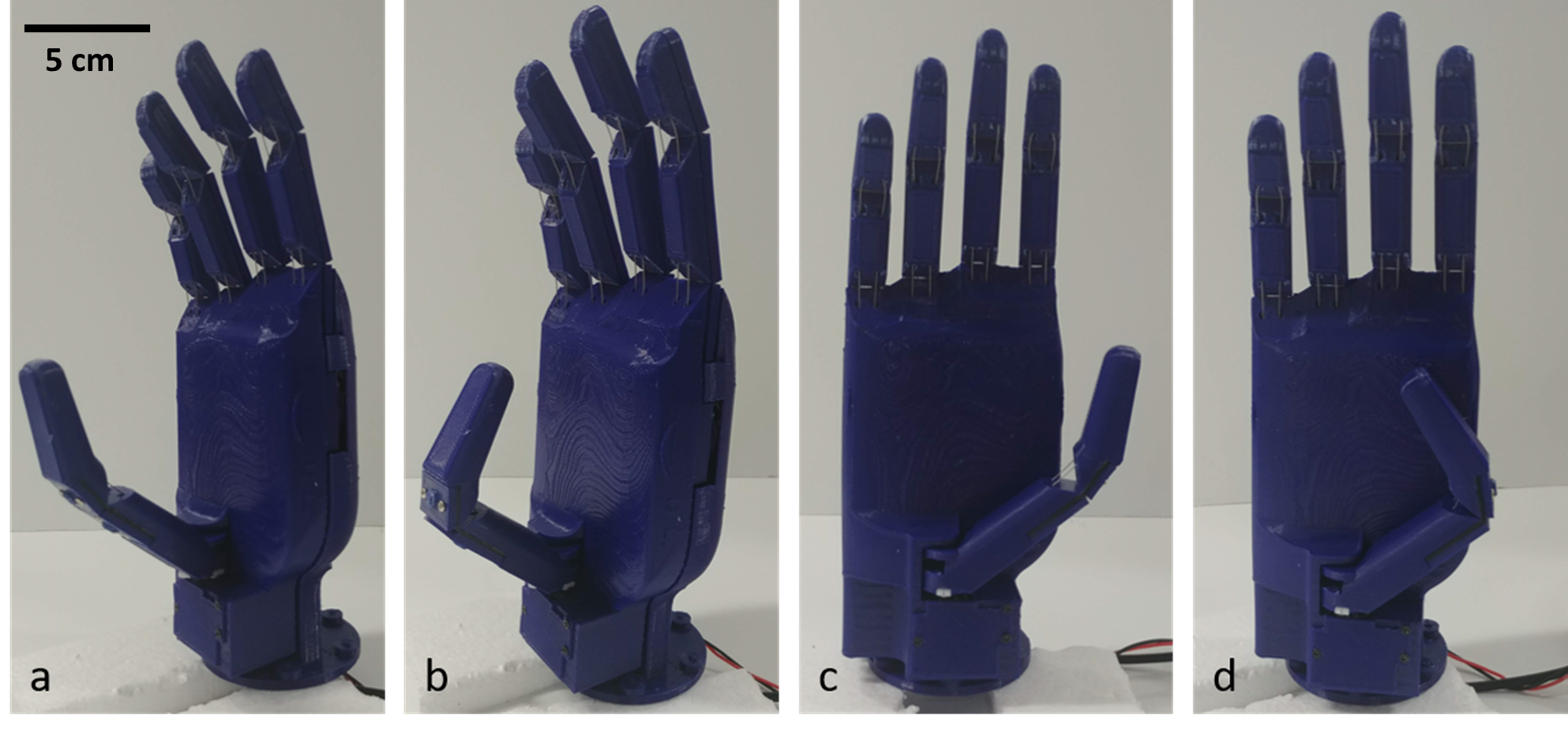
We demonstrate that the optimized hand outperforms a well-known open-source 3D printed anthropomorphic hand on multiple tasks and test the performance of our hand by employing a classification-based user intent decision system which predicts the grasp type using real-time electromyographic (EMG) activity patterns.
Click here for more information